A wide body of evidence substantiates the efficacy of Dexcom Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Systems for insulin-using patients with type 1 diabetes. Dexcom CGM use can help patients meet their HbA1c and Time in Range (TIR) targets, and achieve sustained glycaemic control.1,2,4
Left Column Title
Reduction of HbA1c by 1.0% for Patients with T1D*,1
Reduction of HbA1c by 1.0% for Patients with T1D*,1
Dexcom CGM System users on a multiple daily injections (MDI) insulin regimen showed an average A1C reduction of 1% after 24 weeks of regular use, compared to baseline. Additionally, 52% of subjects in the study had a ≥1% A1C reduction.1


Right Column Title
Increased Time in Range
Increased Time in Range
In a recent clinical trial, rt-CGM helped patients increase the amount of time in range (TIR) by an average of nearly five hours per day, independent of insulin delivery method. 2
Left Column Title
Reduction in Hypoglycaemia
Reduction in Hypoglycaemia
Hypoglycaemia presents a significant risk to the health and safety of your patients. Not only can Dexcom CGM use reduce A1C, but numerous studies have also shown it can also decrease time spent in hypoglycaemia.1,4-8
Right Column Title
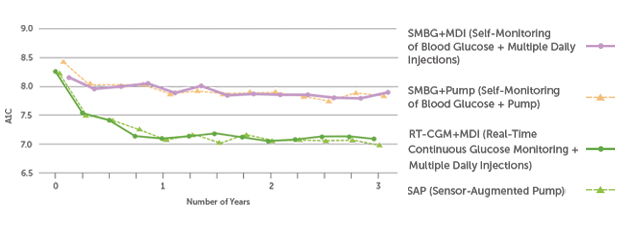
Patients Show Sustained HbA1c Reduction with Long-Term Real-Time CGM (rt-CGM) Use
Patients Show Sustained HbA1c Reduction with Long-Term Real-Time CGM (rt-CGM) Use
A three-year, real-world clinical trial—the longest CGM outcome study to-date—reiterates the clinical impact of using real-time CGM (rt-CGM) systems like Dexcom G6.
Study participants with T1D using rt-CGM showed significantly reduced A1C levels, increased TIR (3.9-10.0 mmol/L), and decreased time below range (<3.9 mmol/L), independent of insulin delivery method.2
Left Column Title
Increased quality of life
Increased quality of life
Patients switching to Dexcom CGM report improved overall wellbeing and quality of life scores vs baseline/conventional therapy.4

*Study conducted using the Dexcom G4® PLATINUM CGM System, which uses the same software as the Dexcom G5® Mobile CGM System.
1 Beck RW, et al. JAMA. 2017;317(4):371-378.
2 Šoupal J, et al. Diabetes Care 2020;43:37–
4 Lind M, et al. JAMA 2017;317:379-87.
5 Heinemann L, et al. Lancet 2018;391:1367-77.
6 Riddlesworth T, et al. Diabetes Ther 2017;8:947-51.
7 Reddy M, et al. Diabet Med 2018;35:483-90.
8 Reddy M, et al. Diabetes Technol Ther 2018;20:751-57.